
Vector-borne infectious diseases have been identified more frequently in humans and domestic animals in recent years, and include some of the most important emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases.

Vector-borne infectious diseases have been identified more frequently in humans and domestic animals in recent years, and include some of the most important emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases.

Feline herpesvirus-1 (FHV1) and feline calicivirus (FCV) are the two major viral causes of upper respiratory tract disease (URD) in cats.

Distemper is very contagious disease of dogs that may involve the gastrointestinal, respiratory and/or neurologic systems.

Despite improvements in our understanding of the pathogenesis of FIP, FIP remains a leading cause of death in young cats, especially purebred catteries, shelters.

Causes of anemia in cats include decreased red blood cell (RBC) production, blood loss, and increased RBC destruction.

Immunosuppression in pets may be the result of an acquired immune deficiency, such as that due to neoplastic disease, immune-mediated disease, endocrine disease, or drug therapy; or more rarely, a congenital immune deficiency.
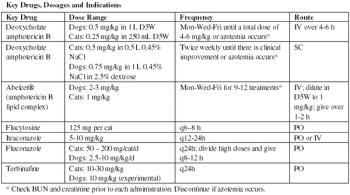
In recent years, the use of antifungal drugs in human medicine has increased, especially with the advent of the AIDS epidemic.

PCR-based diagnosis is ideally suited to detection of organisms that are not easily found on cytologic preparations, are slow-growing or difficult to cultivate, when a rapid diagnosis is required, when alternative methods are expensive or hazardous to laboratory staff, or when inhibitory substances such as antimicrobials may be present.

Leptospirosis is caused by infection with serovars of Leptospira interrogans sensu lato.

Published: April 1st 2008 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2008 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2008 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2008 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2008 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2008 | Updated: