Articles by James England, DVM

Vaccine types, delivery methods and adjuvants in use in veterinary medicine have been relatively static for many years and limited to modified live organism and killed organism (KV) vaccines, needle injection and alum-type and water –in-oil emulsion adjuvants.
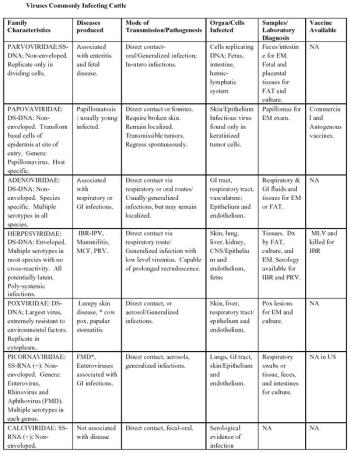
Animal viruses are now classified into 16 separate families.

Complete herd health programs should be a mainstay of production animal practice; however, I find these programs are rarely revisited by the veterinarian and the producer resulting in "antigenic shift" towards unrealistic programs for which the veterinarian is still considered the source.

Infectious conditions like respiratory diseases, reproductive diseases and neonatal diarrheas continue to "plague" animal owners.
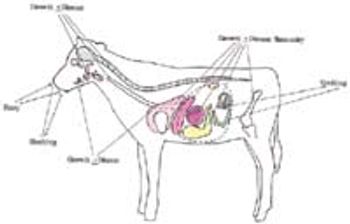
Direct transmission requires that animals be in close, intimate contact because the animal-free state of the virus must be very short in order to effect a successful transmission of viable virus.

When I report back to a cattle owner that his animal is "BVD positive," before I can even begin to explain what that means, I am all to often asked "what is BDD, BV . . . what?" since I am usually talking to the rancher about a normal calf , not an obviously sick animal.







