Elizabeth Rozanski, DVM, DACVIM, DACVECC
Articles by Elizabeth Rozanski, DVM, DACVIM, DACVECC

Traumatic thoracic injuries are prevalent in small animals, particularly in dogs. The most common causes of thoracic trauma are motor vehicular accidents and bite wounds. Other possible, although less common mechanisms include gunshot, knife wounds or being kicked by a larger animal (horse/cow). Injuries may range from mild to life threatening.

Tracheal stenting has been recently re-introduced as an approach to management of severe tracheal collapse. Severe tracheal collapse is life-threatening and while extra-thoracic collapse may be amenable to extra-luminal prosthetic rings, intra-thoracic collapse is not.
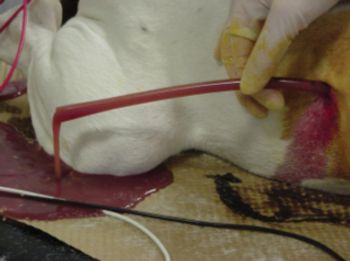
The purpose of this lecture is to review the management of pyothorax in cats and dogs. Pulmonary infection can result from bacterial, viral, fungal or protozoal infection, however, pyothorax is almost uniformly bacterial. The pleural space has a small amount of fluid normally (~ 5 ml) which serves as lubrication for the pulmonary parenchyma.
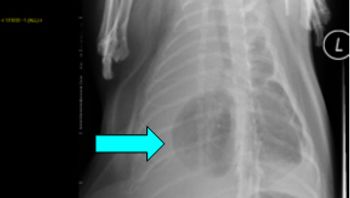
Pneumothorax is defined as free air in the pleural space. Normal intra-pleural pressure is about - 5 cmH20, which means that in order to equilibrate pressures, air from either the atmosphere, or the lung will equilibrate rapidly with the pleural space. Pneumothorax can be further characterized as traumatic, spontaneous and iatrogenic.

Respiratory distress is common and challenging. Cats often compensate well for pulmonary diseases, and some conditions can rapidly fulminate. Dogs are often more "honest" although they can decompensate rapidly as well. It is crucial to balance the equal goals of limiting stress on the patient with respiratory distress, and to work to identify the specific cause of the distress so that appropriate therapy can be provided.
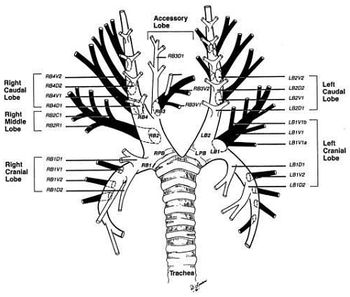
Definitive diagnosis of pulmonary disease remains elusive at times. Cytological or histopathological samples are useful to help better classify the underlying cause as well as determine both prognosis and treatment course. Thus, it is prudent for the criticalist to have a strong grasp of the various techniques and options available for sampling.

Upper airway diseases/obstruction are relatively common causes of respiratory distress in dogs and cats. However, because lung parenchymal diseases are more frequently observed, upper airway problems may be overlooked. In order to fully appreciate upper airway disease, it is essential to be familiar with the structure, function, and common abnormalities.
Evaluation of the pet with respiratory disease may be challenging. The best approach to problem solving usually reflects first an assessment for immediate intervention, and then careful evaluation to localize the problem, and then finally determination of the specific problem and the available options for controlling or curing it. Immediate intervention is warranted in any pet that is having difficulty breathing.

Traumatic thoracic injuries are prevalent in small animals, particularly in dogs. The most common causes of thoracic trauma are motor vehicular accidents and bite wounds. Other possible, although less common mechanisms include gunshot, knife wounds or being kicked by a larger animal (horse/cow). Injuries may range from mild to life threatening.
Blood gas, electrolyte and lactate analysis are very useful in management of the ill or injured dog or cat. Knowledge of normal values and what they indicate can help improve patient care and understanding of the pathophysiological changes accompanying critical illness.
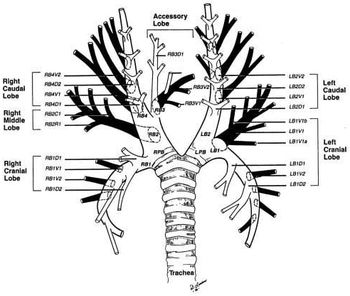
Definitive diagnosis of pulmonary disease remains elusive at times. Cytological or histopathological samples are useful to help better classify the underlying cause as well as determine both prognosis and treatment course. Thus, it is prudent for the criticalist to have a strong grasp of the various techniques and options available for sampling.
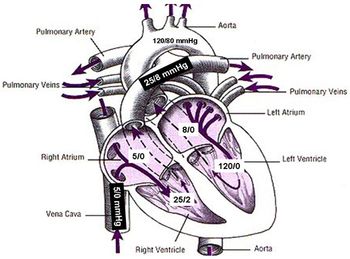
Pulmonary vascular disease or pulmonary vascular obstructive disease (PVOD). is a catch-all term for conditions that affect the pulmonary circulation. These conditions are of particular importance to as they may result in severe respiratory dysfunction. As a review, the pulmonary and systemic circulation are in series, with the cardiac output of the left and right heart (in the absence of cardiac shunt) being equal.

The pleural space is defined as the area between the lungs and the chest wall. Normally there is no soft tissue or free air present in this space. A very small amount of fluid (undetectable on radiographs or ultrasound) may be present within the thoracic cavity. Clinical signs of pleural space disease include tachypnea or difficulty breathing.
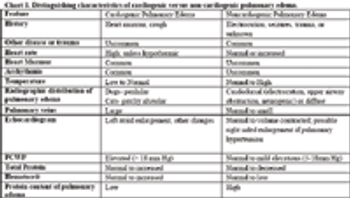
Pulmonary edema is defined as the accumulation of abnormal amount of extravascular lung water. Pulmonary edema may range from clinically insignificant to life-threatening. Pulmonary edema forms when there is an alternation in the balance of Starling forces (hydrostatic and colloid osmotic) between the interstitium and pulmonary capillary beds that favors increasing filtration to the interstitium. Increased capillary hydrostatic forces will result in a low protein edema fluid while lowered colloid osmotic forces will promote a high protein edema fluid.

Cough is a common presenting complaint for dogs and, to a lesser extent, cats. Cough is a sign of an underlying disorder, not a primary disease. Therefore, the cause of the cough should be identified and the underlying disease, not just the cough, should be treated.

Treating animals with respiratory distress may be very challenging. It is essential for the practitioner to have a strong knowledge base of available therapeutic and diagnostic techniques. It is also prudent to be prepared for any potential complications that may develop during diagnostic or therapeutic interventions.

Evaluation of the pet with respiratory disease may be challenging.

The pleural space is defined as the area between the lungs and the chest wall.

Traumatic thoracic injuries are prevalent in small animals, particularly in dogs.

Treating animals with respiratory distress may be very challenging.

Cough is a common presenting complaint for dogs and, to a lesser extent, cats.

Pulmonary edema is defined as the accumulation of abnormal amount of extravascular lung water.
Blood gas, electrolyte and lactate analysis are very useful in management of the ill or injured dog or cat. Knowledge of normal values and what they indicate can help improve patient care and understanding of the pathophysiological changes accompanying critical illness.

Treating animals with respiratory distress may be very challenging.
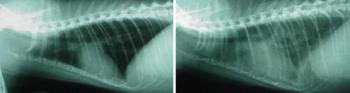
Cats with respiratory distress represent a significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenge to the small animal veterinarian.

Cough is a common presenting complaint for dogs and, to a lesser extent, cats.
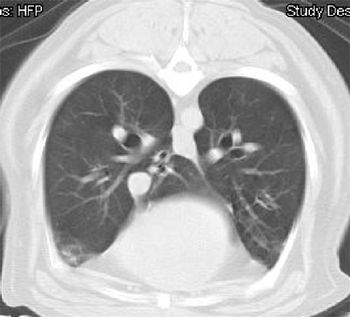
Interstitial lung disease represents a diffuse subset of pulmonary disease that includes abnormalities in the microscopic interstitium (the anatomic space between the basement membranes of the epithelial and endothelial cells) as well as the inflammatory and/or fibrotic processes that extend into the alveolar space, as well as the bronchioles and bronchiolar lumen.
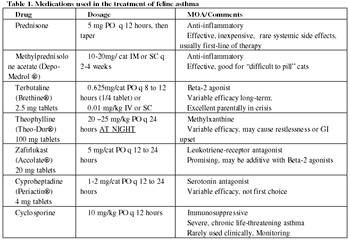
Asthma is a common, although poorly defined, condition in cats.

The pleural space is defined as the area between the lungs and the chest wall.

Upper airway diseases/obstruction are relatively common causes of respiratory distress in dogs and cats.


















